Databricks
Amplitude's Databricks import source enables you to import data from Databricks to your Amplitude account. Databricks import uses the Databricks Change Data Feed (CDF) feature to securely access and extract live data from your Databricks workspace.
For guided instructions to setting up this integration, view the Loom video.
Features
- Import events, user properties, profiles, and group properties.
- Support for delta sync to ensure Amplitude imports only new or changed data.
Limitations
-
The User Look-Up page doesn't display 100 most recent events ingested.
-
The following Databricks features don't support time travel, and aren't supported by this integration:
-
SQL input restrictions for Mirror Sync change data feed type:
- Only one source Delta Table (referred to as “main table”)
- Single SELECT statement
- Common Table Expressions (CTE) (for example, WITH-clause) aren't supported
- Set operations like
UNION,INTERSECT,MINUS, andEXCEPTaren't supported - Statements with a
JOINclause use mutation metadata from the main table, ignoring the mutation history of the joined table. Amplitude uses the latest version of data in the joined table during data synchronization. - Explicit SQL validation may not cover all edge cases. For example, if you provide more than one source table, validation may succeed during source creation, but fail during import execution.
-
User Privacy API: The User Privacy API deletes previously ingested data and doesn't prevent Amplitude from processing new information about a user. When you use CDF, you must stop sending data about a user before you delete them with the User Privacy API. This ensures that Amplitude doesn't recreate the user in the next sync.
To delete all data associated with an end-user from Amplitude's systems, deleting the user from your data warehouse isn't enough. This process requires a User Privacy API request to ensure the user's data is removed from Amplitude's systems
CDF and event volume
INSERT, UPDATE, and DELETE operations to Amplitude based on your sync frequency. This means that multiple operations can be made to an event during the sync window and they only count as one event against your existing event volume. However, any operation made to an event outside of the sync window counts as an additional event against your existing event volume. This may impact the rate at which you use your existing event volume. Contact sales to purchase additional event volume, if needed.- Mirror Sync events and mutations don't support unknown users. Rows must contain a user id or Amplitude drops the event. If you have a high volume of anonymous events, Amplitude recommends against using this mode.
Configure Databricks
Before you start to configure the Databricks source in Amplitude, complete these tasks in Databricks:
Find or create an all-purpose compute cluster
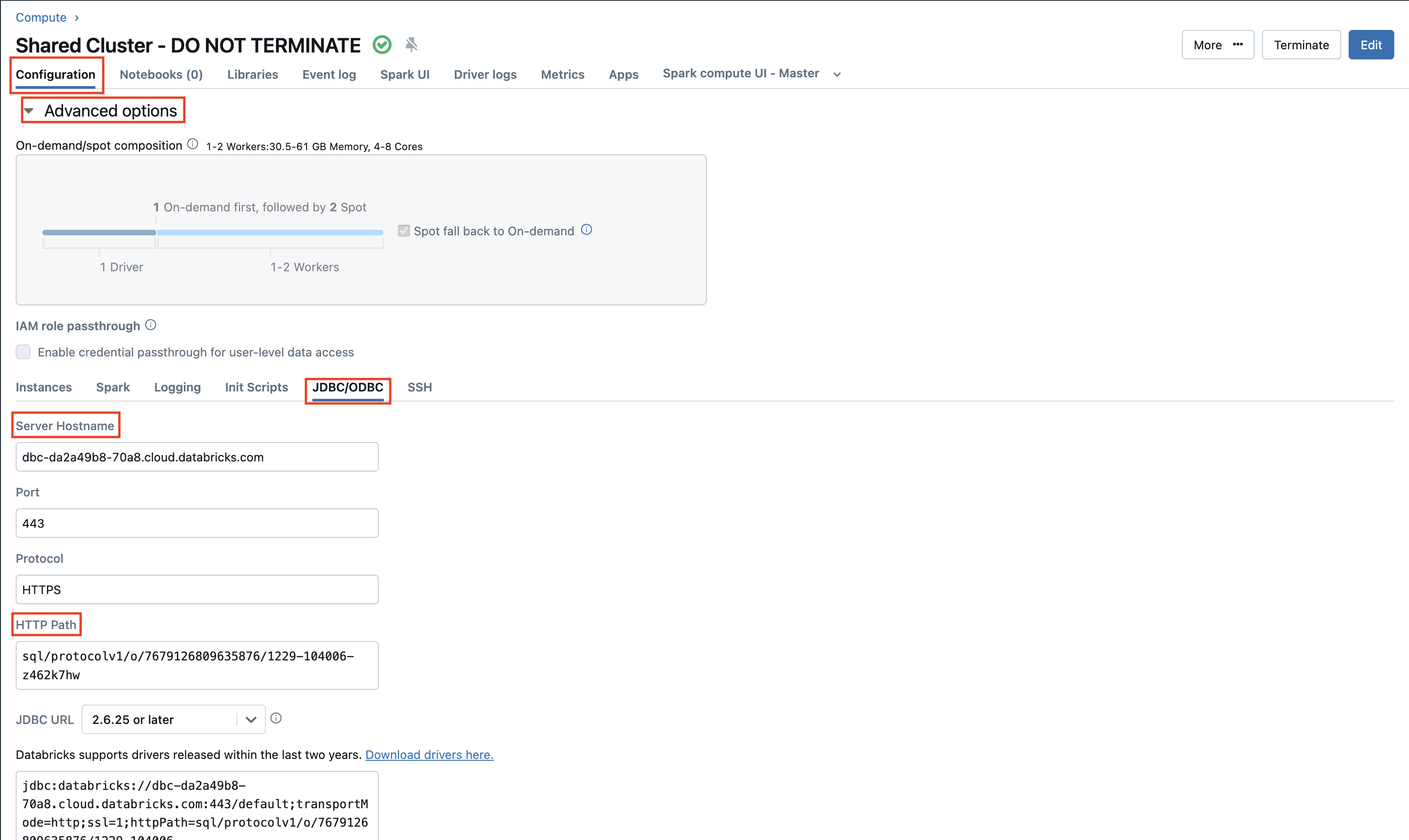
Amplitude creates workflows in this cluster on your behalf to start sync jobs. When complete, copy the server hostname and HTTP path values to use in a later step. Find both values on the Configuration -> JDBC/ODBC tab. For more information about cluster types, see Compute.
Note
"workload_type.clients.jobs": {
"type": "fixed",
"value": false
}
Note
TypeError: 'type' object is not subscriptable
Cluster policies and access modes
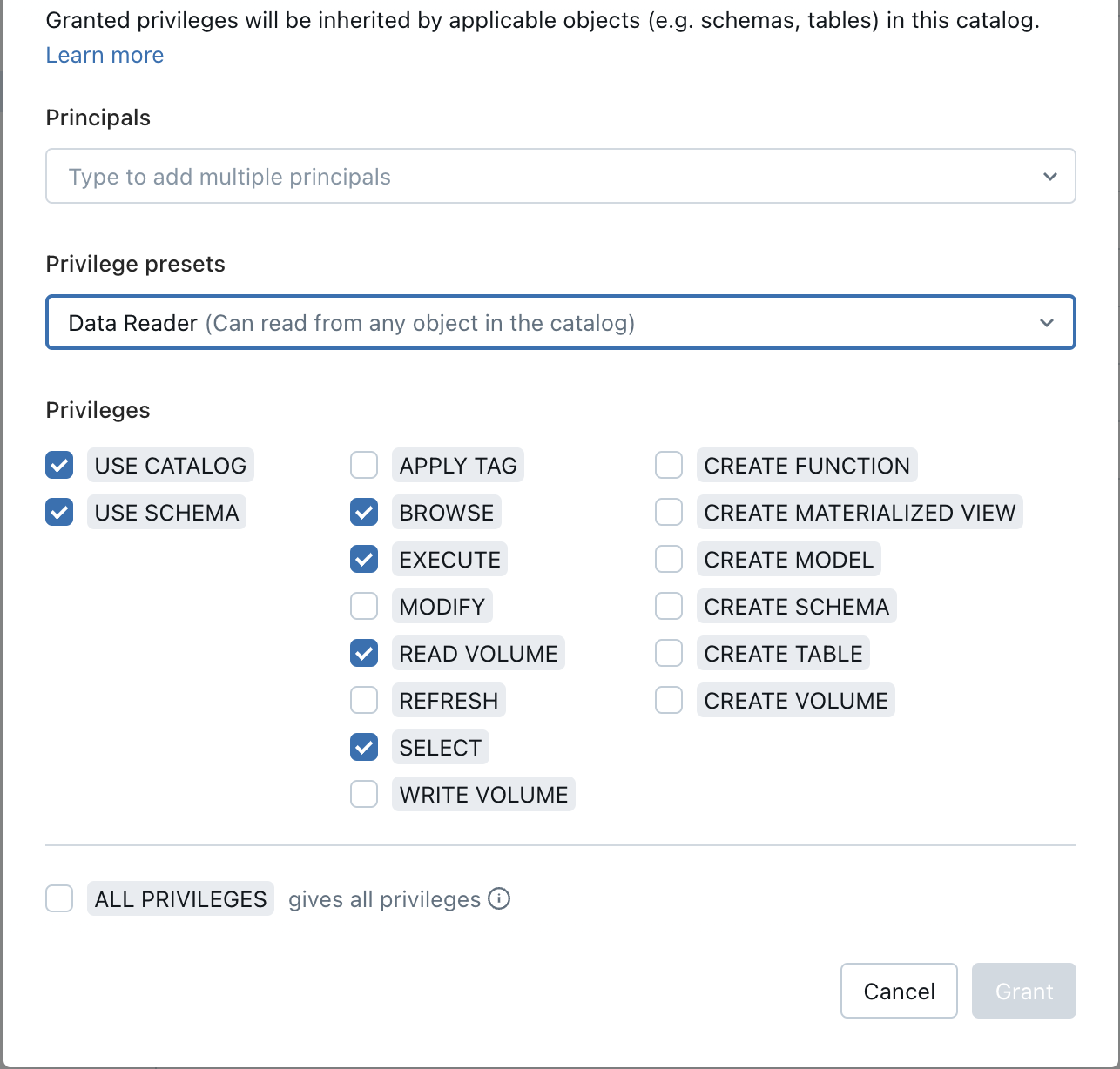
Amplitude supports all policies and access modes. However, if your clusters have the following policies and access modes, grant the Data Reader permission (USE CATALOG, USE SCHEMA, EXECUTE, READ VOLUME, SELECT) to the your workspace user or service principal, whose personal access token is used to authenticate in Amplitude. Otherwise, you can't access the tables in the unity catalog of your import source.
AWS Databricks:
| Policy | Node | Cluster Access mode |
|---|---|---|
| Unrestricted | Multi node | No isolation shared |
| Unrestricted | Single node | No isolation shared |
| Power User Compute | N/A | No isolation shared |
| Legacy Shared Compute | N/A | N/A |
GCP Databricks:
| Policy | Node | Cluster Access mode |
|---|---|---|
| Unrestricted | Multi node | No isolation shared |
| Unrestricted | Single node | No isolation shared |
| Power User Compute | N/A | Shared |
| Power User Compute | N/A | No isolation shared |
| Legacy Shared Compute | N/A | N/A |
Authentication
Amplitude's Databricks import supports authentication with personal access tokens for Databricks workspace users, or personal access tokens for Service Principals. Choose Workspace User authentication for faster setup, or Service Principal authentication for finer grained control. For more information, see Authentication for Databricks Automation
Create a workspace user personal access token (PAT)
Amplitude's Databricks import uses personal access tokens to authenticate. For the quickest setup, create a PAT for your workspace user in Databricks. For more information, see Databricks' article Personal Access Tokens for Workspace Users
Create a service principal personal access token (PAT)
Amplitude recommends that you create a service principal in Databricks to allow for more granular control of access.
-
Follow the Databricks instructions to create a service principal. Copy the UUID for use in a later step.
-
Generate a PAT on this Service Principal.
- If you use AWS or GCP Databricks, follow the instructions in the article Databricks personal access tokens for service principals.
- If you use Azure-based Databricks, follow the instructions in the article Manage personal access tokens for a service principal.
The service principal you created above requires the following permissions in Databricks:
| Permission | Reason | Location in Databricks |
|---|---|---|
| Workspace | Grants access to your Databricks workspace. | Workspace → <workspace_name> → Permissions → Add permissions Add the service principal you create with the User permission, click Save. |
| Table | Grants access to list tables and read data. | Catalog → pick the catalog→ Permissions → Grant Select the Data Reader permission (USE CATALOG, USE SCHEMA, EXECUTE, READ VOLUME, SELECT). |
| Cluster | Grants access to connect to the cluster and run workflows on your behalf | Compute → All-purpose compute → Edit Permission Add the Can Restart permission to the service principal. |
| Export | Enables the service principal to unload your data through spark and export it to S3. | Run the SQL commands below in any notebook: GRANT MODIFY ON ANY FILE TO `<service_principal_uuid>`; GRANT SELECT ON ANY FILE TO `<service_principal_uuid>`; |
Enable CDF on your tables
Amplitude uses the Databricks Change Data Feed to continuously import data. To enable CDF on a Databricks table, see Databricks | Enable change data feed
Configure the Amplitude Databricks source
To add Databricks as a source in Amplitude, complete the following steps.
Connect to Databricks
- In Amplitude Data, navigate to Catalog -> Sources.
- Search for Databricks.
- On the Credentials tab of the Connect Databricks screen, enter the credentials you configured during the Databricks configuration:
- Server hostname
- HTTP Path
- Personal Access Token (for the workspace user or Service Principal)
- Click Next to verify access.
Select data to import
-
Select the data type for data to be imported. The Databricks source supports three data types:
-
If you selected
Eventas the data type, choose the import strategy:
- Append Only Sync: Ingest data warehouse data with Amplitude's standard enrichment services like ID resolution, property and attribution syncing, and resolving location info.
- Mirror Sync: Directly mirror the data in Databricks with insert, update, and delete operations. This deactivates Amplitude's enrichment services to remain in sync with your source of truth.
-
Configure the SQL command that transforms data in Databricks before Amplitude imports it.
- Amplitude treats each record in the SQL execution output as an event to be import. See the Example body in the Batch Event Upload API documentation to ensure each record you import complies.
- Amplitude can transform / import from only the tables you specify in step 1 above.
- For example, if you have access to tables
A,BandCbut only selectedAin step 1, then you can only import data fromA.
- For example, if you have access to tables
- The table names you reference in the SQL command must match exactly the name of the table you select in step 1. For example, if you select
catalog.schema.table1, use that exact value in the SQL.
select unix_millis(current_timestamp()) as time, id as user_id, "demo" as event_type, named_struct('name', name, 'home', home, 'age', age, 'income', income) as user_properties, named_struct('group_type1', ARRAY("group_A", "group_B")) as groups, named_struct('group_property', "group_property_value") as group_properties from catalog.schema.table1;
VARIANT data type support
VARIANT data type for mapping property columns. You can use VARIANT columns for user properties, event properties, and group properties in your SQL queries. This allows you to import semi-structured or nested JSON data directly from Databricks.For the Event data type and Append-Only Ingestion, optionally select Sync User Properties or Sync Group Properties to sync the corresponding properties within an event.
-
After you add the SQL, click Test SQL. Amplitude runs a test against your Databricks instance to ensure the SQL is valid. Click Next.
-
Select the table version for initial import. The initial import brings everything the from table as of the selected version. Select First or Latest.
Firstmeans first version, which is 0.Latestmeans latest version.
-
Set the sync frequency. You can configure the sync frequency when setting up a source. This frequency determines the interval at which Amplitude pulls data from Databricks.
The available sync frequency options vary depending on the data type you're importing, such as Events, User Properties, Group Properties, and Profiles. Examples:
- Daily sync: Runs once each day at a specified hour.
- Hourly sync: Runs once each hour.
Amplitude runs syncs on a best-effort basis. Syncs typically run at the configured frequency but may run less frequently.
-
Enter a descriptive name for this instance of the source.
-
The source appears in the Sources list for your workspace.
Verify data import
Events that Amplitude imports assume the name you assign in your SQL statement. In the example above, the events have the name demo
To verify the data coming into Amplitude:
- View the Events page of your Tracking Plan
- Create a Segmentation chart that filters on the event name you specify.
- Go to the
Ingestion Jobstab in your source. You can view the status of the ingestion and debug usingERROR LOGif necessary.
Depending on your company's network policy, you may need to add the following IP addresses to your allowlist to allow Amplitude's servers to access your Databricks instance:
- Amplitude US IP addresses:
- 52.33.3.219
- 35.162.216.242
- 52.27.10.221
- Amplitude EU IP addresses:
- 3.124.22.25
- 18.157.59.125
- 18.192.47.195
Troubleshooting
-
shaded.databricks.org.apache.hadoop.fs.s3a.AWSClientIOException: getFileStatus on s3a://com-amplitude-falcon/databricks_import/unloaded_data/source_destination_158631/batch_712300169/meta: com.amazonaws.SdkClientException: Unable to execute HTTP request: Remote host terminated the handshake: Unable to execute HTTP request: Remote host terminated the handshake --------------------------------------------------------------------------- Py4JJavaError Traceback (most recent call last) File /databricks/spark/python/pyspark/errors/exceptions.py:228, in capture_sql_exception.<locals>.deco(*a, **kw) 227 try: --> 228 return f(*a, **kw) 229 except Py4JJavaError as e:- Root cause 1: This error is caused by a limitation of clusters running in shared access mode due to their additional security hardening measures.
- Solution 1: Use a cluster configured with either single-user or no-isolation shared access mode.
- Root cause 2: For Azure Databricks, this issue could be caused by firewall settings where the Databricks cluster can't access the Amplitude s3 bucket.
- Solution 2: See if there are any network rules blocking Databricks clusters from accessing Amplitude s3 bucket.
-
[Databricks][JDBCDriver](500593) Communication link failure. Failed to connect to server. Reason: HTTP Response code: 403, Error message: PERMISSION_DENIED: You do not have permission to autostart 0108-111840-mc2khhh6.. isCausedByCustomer=true,isAutomaticallyRecoverable=false,errorType=databricks-jdbc-connection-error.- Root cause: This error occurs when Amplitude attempts to establish a JDBC connection with your all-purpose cluster. If the cluster is terminated, Databricks automatically tries to restart it, resulting in a permission error if the PAT lacks sufficient privileges to start the cluster.
- Solution: Create a service principal access token with the Can Restart permission and assign it to the user on the cluster to allow access.
-
java.sql.SQLException: [Databricks][JDBCDriver](500593) Communication link failure. Failed to connect to server. Reason: HTTP Response code: 502, Error message: Unknown.- Root cause: Either the driver or executors may be unresponsive due to high memory use. When the memory is full, the driver/executor becomes unresponsive for a few seconds during garbage collection to free memory. This can sometimes cause the communication link failure seen above.
- Solution: Either 1) optimize the workloads and underlying tables to use less memory, 2) increase the memory of the driver or 3) increase the limit of max workers so the cluster can add more workers during moments of heavy resource contention.
-
Caused by: java.sql.SQLException: [Databricks][JDBCDriver](500593) Communication link failure. Failed to connect to server. Reason: HTTP Response code: 554, Error message: Service is under maintenance..- Root cause: Issue on the Databricks Proxy API.
- Solution: Escalate to Databricks support.
-
Py4JJavaError: An error occurred while calling o450.isEmpty. : com.databricks.sql.transaction.tahoe.DeltaFileNotFoundException: [DELTA_EMPTY_DIRECTORY] No file found in the directory: s3- Root cause: The delta log is truncated and expired, so the Amplitude service didn't find a delta log file to import.
- Solution: Contact Amplitude support to skip expired data and continue the import. By default, retention is 30 days, make sure to keep the data for at least 7 days.
-
Fail worker job since databricks job run finished with state MAXIMUM_CONCURRENT_RUNS_REACHED.- Root cause: Your Databricks job allows only one run at a time. If you trigger a new job while a previous run is still in progress, Databricks skips it.
- Solution: Update the Databricks job configuration to increase the maximum concurrent runs.
-
[Databricks][JDBCDriver](700100) Connection timeout expired. Details: None.- Root cause: This means Amplitude was unable to establish a JDBC connection to the Databricks endpoint. It often occurs because:
- The Databricks cluster was terminated and is taking too long to restart, causing the connection attempt to time out.
- The Databricks workspace may have reached resource limits (for example, maximum concurrent SQL endpoints, cluster quota, etc).
- Solution:
- Check the Databricks workspace and cluster status to confirm whether the cluster was terminated or is restarting during the connection attempt.
- Review cluster auto-start and auto-termination settings to ensure clusters can restart quickly when needed.
- Monitor for resource limits in Databricks (such as concurrent connection caps or cluster capacity issues) and adjust quotas if necessary.
- Root cause: This means Amplitude was unable to establish a JDBC connection to the Databricks endpoint. It often occurs because:
-
[DELTA_MISSING_CHANGE_DATA] Error getting change data for range [2 , 3] as change data was not recorded for version [2]- Root cause: This means Amplitude couldn't retrieve data from the table for a specific version range. It occurs because:
- Change data feed(CDF) was enabled after the specific table version, so the change data doesn't exist for the range.
- The specific table version has been vacuumed and corresponding data files have been deleted.
- Solution:
- Create a new source which starts importing from the latest table version.
- If you want to reuse the same source and skip the table version, contact Amplitude Support.
- Root cause: This means Amplitude couldn't retrieve data from the table for a specific version range. It occurs because:
September 19th, 2024
Need help? Contact Support
Visit Amplitude.com
Have a look at the Amplitude Blog
Learn more at Amplitude Academy
© 2026 Amplitude, Inc. All rights reserved. Amplitude is a registered trademark of Amplitude, Inc.