Root Cause Analysis: Track down anomalies in your data
When working with product analytics, understanding why something is happening is arguably more important than understanding what is happening in the first place. This is especially true when Amplitude is showing anomalous data. As in, events and properties that are out of the ordinary, and to a significant extent. With anomalous data, you need to be able to determine if what you're seeing is just a random blip, or the beginning of a shift in the way your users interact with your product.
Historically, that insight has not always been easy to come by. For example, it would take a decent amount of guesswork to navigate down the hierarchy from Platform → OS → Device family to finally discover that an observed change is driven by users on a specific type of device.
Amplitude's Root Cause Analysis (RCA) feature addresses this by analyzing the properties of the anomalous events for you, while also pulling in external context like country-specific holidays and new releases of your product. In this way, it can potentially explain the anomaly or rule out the obvious. It's designed to streamline your workflow and help you quickly understand the “why?” of a change, so that you can easily answer questions like “Which user groups best explain this change?” or “How are other correlated metrics affected?”
- This feature is supported for Event Segmentation charts only. It cannot be used with formulas.
Analyze an anomalous data point
In order to use RCA, you must first have an analysis in Amplitude that's displaying anomalous data.
For example, this Event Segmentation chart has an unusual-looking peak for December 30th:
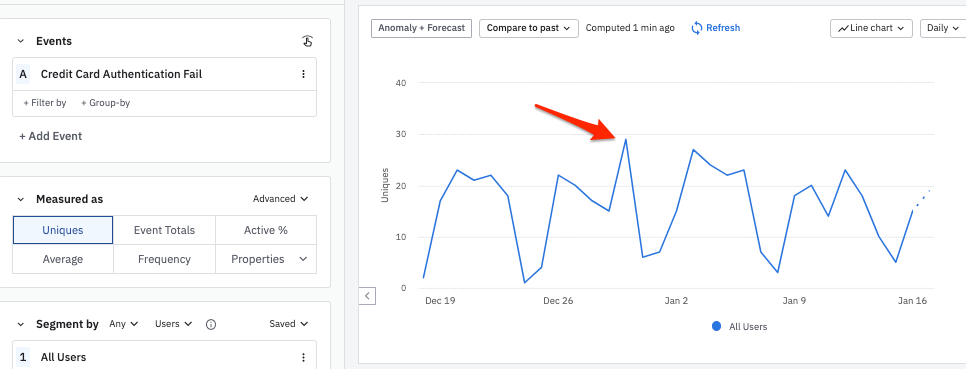
To examine this anomalous data point using Root Cause Analysis, follow these steps:
-
Click Anomaly + Forecast to confirm that the result you're interested in is actually a statistical anomaly. Amplitude enhances the chart to display the statistically-expected values for each day, as well as a range of values that would not be considered anomalous (in other words, values that could be attributable to random chance).
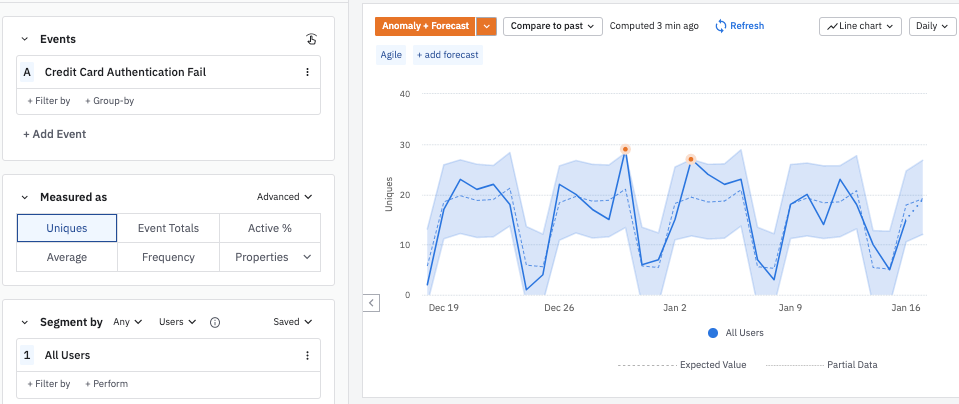
In this example, the December 30th data point is inside the range of statistically "normal" values—but only just.
-
Click on the data point to bring up the Microscope. Then click Run Root Cause Analysis. Scroll down to view the Root Cause Analysis tab.
At this point, Amplitude scans the properties of the anomalous event and compare them to a baseline. It then generates a time-series graph for each property, so you can understand how each value tracks with the anomalous data point.
You can expand any of these graphs into a standalone Event Segmentation chart by clicking Open Chart for the graph you're interested in.
You can also give feedback on the chart by clicking the thumbs-up or thumbs-down icon. This tells Amplitude whether you found the chart useful or not, and helps improve the ranking algorithm over time.
RCA scans event properties in batches of thirty, in order to present you with results for the most relevant properties first. From time to time, RCA automatically pausees scanning, so as to avoid overwhelming you with graphs. If you want RCA to scan more properties, click Continue Scanning.
Tip
Configure your analysis
Amplitude automatically starts scanning with the thirty most-queried properties. If you'd like a specific event property to be included in future scans, click Configure to open the Configure Analysis modal. Then click Select property... and select the property you're interested in from the list.
June 6th, 2024
Need help? Contact Support
Visit Amplitude.com
Have a look at the Amplitude Blog
Learn more at Amplitude Academy
© 2026 Amplitude, Inc. All rights reserved. Amplitude is a registered trademark of Amplitude, Inc.