What Is Product Development? Steps, Best Practices, and Examples
Learn the basics of the product development process.
Browse by category
- What is product development?
- Who’s responsible for the product development process?
- The 6 key stages of product development
- Why product development is not the same as product management
- Product development best practices (with advice from product leaders)
- Popular product development frameworks
- Data-driven product development examples
- Top 5 product development tools
- Analytics are crucial for excellent product development
Product development is the process of launching effective, well-researched, and in-demand products. Taking a product from its initial idea to a successful launch involves several steps, including research and prototyping. Products typically go through rounds of iteration and testing before they’re released to users.
Key takeaways
- Product management focuses on defining what product to build, while product development is about executing the vision and building the product.
- The product development process includes six key stages: research and idea generation, product scope definition, product roadmap creation, concept prototyping, execution and testing, and market entry.
- Key roles in product development include product developers, engineers, product managers, UX/UI designers, and project managers, with contributions from customer support and sales.
- Best practices include centering on customer needs, embracing data to inform decisions, and prioritizing testing and experimentation.
What is product development?
Product development is the journey a product takes from conception to market release. Product teams work together to research, create a roadmap, prototype the product, conduct testing, and get customer feedback before launching the product in collaboration with marketing. A successful product meets a market need and fulfills customers’ expectations, so each step in the process is essential.
Who’s responsible for the product development process?
The quality of the finished product has a big impact on a company’s success—especially those companies with a product-led motion, where the product is the center of acquisition and retention strategies. Given the importance of the product, many roles are typically involved in the development process, including:
- Product developers and engineers: the product development team who will build and test the product.
- Product managers: responsible for defining the product’s strategy and vision. They’ll coordinate with the product engineers and collaborate with other stakeholders.
- UX and UI product designers: collaborate with product developers to shape the product’s front end and customer experience.
- Project managers: organize the logistics around product development, like budget and timeline, and ensure the product hits production milestones on time.
Other teams, like customer support or sales, may also inform the product roadmap by sharing pain points that your target market is dealing with. Typically, different stakeholders throughout the organization, including leadership, will be involved in the development process by sharing feedback at different stages.
The 6 key stages of product development
Any new product or product improvement will go through a product development process to ensure the idea is viable and the end product is effective. Each step in this process is important, and some—such as testing—may be repeated until the result is satisfactory.
1. Research and idea generation
Start new product development by brainstorming new product ideas or approaches to improving an existing product. Base ideas on market research, customer needs, product functionality, and pricing. Aim to identify a market need where your product can fill a gap. You can use ideation frameworks, such as a SWOT analysis, to guide this process.
2. Product scope definition
Refine the product concept and start creating a product strategy. At this stage, you’ll want to:
- Consider the feasibility of the software development involved.
- Conduct business analysis to make sure the project is viable.
- Define the value proposition to be clear about the problem your product is solving.
- Identify what metrics will define success for the project.
- Think about your messaging and product marketing strategy.
3. Product roadmap creation
The roadmap is a high-level overview of the vision and strategy you’ve established that aligns all internal stakeholders on your product development process. It specifies what you’re building and why. It lists product requirements and ties them into the company’s strategic goals.
4. Concept prototyping
Begin prototyping and developing to create a minimum viable product (MVP). An MVP has the minimum functionality—it is used to identify flaws and conduct market testing to gain initial feedback. Prototyping your product enables you to identify problems and areas of opportunity earlier in the process, saving your team from having to redo advanced work.
5. Execution and testing
Execute the concept, working through any issues uncovered during prototyping and testing. Developers focus on making sure the product has all the features it needs and can be scaled to serve an entire community of users. Base development on accurate product and behavioral analytics to keep your team moving in the right direction. Your product will go through multiple iterations as you receive feedback. Testing includes:
- Market testing: Identifies the existing market and customer needs the product meets.
- Customer feedback: Gets feedback from users on the functionality and experience of the product as it’s developing.
- Beta/functionality testing: Uncovers bugs or usability issues with the product.
6. Market entry
When your product is ready for commercialization, launch the final product and marketing campaign. At this point, the design is finalized, fully tested, and ready for implementation. Monitor the metrics you established during product scoping to assess the product’s success and prepare to launch improvements in the future.
Why product development is not the same as product management
Product management is concerned with what product to build, while product development determines how. Product management and product development teams work together, with management plotting the course of the product’s development and development executing it.
Product managers build a strategic roadmap for product development, focusing on conducting market research, analyzing customer feedback, and translating that research into product requirements (all while following these product management best practices). The product development team executes that roadmap, bringing the product from concept to market. They make sure the product is technically sound and meets quality assurance standards.
Product development best practices (with advice from product leaders)
Across the stages of product development, these insights from product experts will help you succeed.
Define a product strategy that focuses on customer needs
Your product strategy is your research-backed assumption about why your product will succeed against the competition. According to former Amplitude product evangelist John Cutler, a strong product strategy “doesn’t just distinguish your product—it benefits your customers by offering something they can’t find elsewhere in the market.” As you create your product strategy, establish what’s special about your product that’ll help your target audience in a way no other product can.
To do that, it’s important to have a clear understanding of what your customer base needs. This is where customer value chains are helpful. Ask questions about customers’ wants and needs, pain points, and how easily they can navigate your product, and combine that information with hard data from product analytics to guide your product development.
Use data democracy to support effective teamwork
Data is key to product development because it helps you base product decisions on facts rather than opinions. Abid Mohammed, co-founder and chief product officer at Pictory, shares that data is important for Pictory product development: “Trusting data over opinion enables us to be curious and creative, respect each other and our customers, move expeditiously, and be open and transparent.”
With so many stakeholders involved in product development, you don’t want to gatekeep the important data they need to make decisions. Data democratization will relieve pressure on your data teams and help your product teams more deeply understand the information the data team has gathered.
Data democracy is about more than just access. It’s about giving your non-technical teams tools—such as software and educational resources—to work with that data comfortably, ask questions freely, and make decisions informed by that data while they build your product.
Test your way to success
Running tests and experiments is one way to source data to inform your decisions—again, helping you act based on facts. “Science has proven to us over and over again that our gut instinct isn’t always right,” says Wil Pong, head of product for Amplitude Experiment. “Between eight and nine out of 10 bets that we ship don’t yield the wins that we thought they would.” Experimentation helps you land on those rare winning ideas as fast as possible.
Learn more about building a culture of product experimentation in our Build With Confidence guide.
Popular product development frameworks
Product development frameworks are structured approaches that help with parts of the product development process. Here are some popular frameworks.
North Star Framework
The North Star Framework is a way of developing and improving products by focusing on a single North Star metric. The metric captures the core value you deliver to customers. When you work to improve that North Star metric, you drive continuous product improvement that impacts customer happiness.
Minimum viable product
The minimum viable product approach involves only building the minimum product features to deliver customer value. Aim to release your product as soon as possible so you can validate your product ideas and gather feedback. This approach helps teams avoid wasting time and resources getting the product ‘perfect’ with a wide range of features, only to fail after the product launch.
Working backward
The working backward methodology—promoted by Amazon—involves starting product development by creating a press release about the product or feature you’re planning to create. The press release forces you to center your product development around what will benefit your potential customers. If the press release doesn’t seem exciting, it’s probably not worth building that product or feature.
Data-driven product development examples
For inspiration and tips, look at these product development examples from three companies that created efficient processes for their product development plans.
LIFULL HOMES
LIFULL HOMES is a Japanese company that develops multiple products in the real estate industry. Their mission—to help people find a home they’ll love—requires a deep understanding of user behavior. Folks at LIFULL use the Amplitude platform to run experiments and gather insights about their users. Armed with that data, they continuously iterate on their features to improve conversion rates.
HubSpot
HubSpot uses product analytics to build products that are based on user behavior. Their product team uses actionable data on individual user and cohort behavior to iterate their product development effectively and build features that improve the customer experience.
Top 5 product development tools
It takes a lot of iteration, collaboration, and feedback processing to get a product successfully through development. Project development and management software will enable your teams to collaborate on each stage, delegate tasks, tag relevant stakeholders, and have visibility into customer feedback and data.
Amplitude
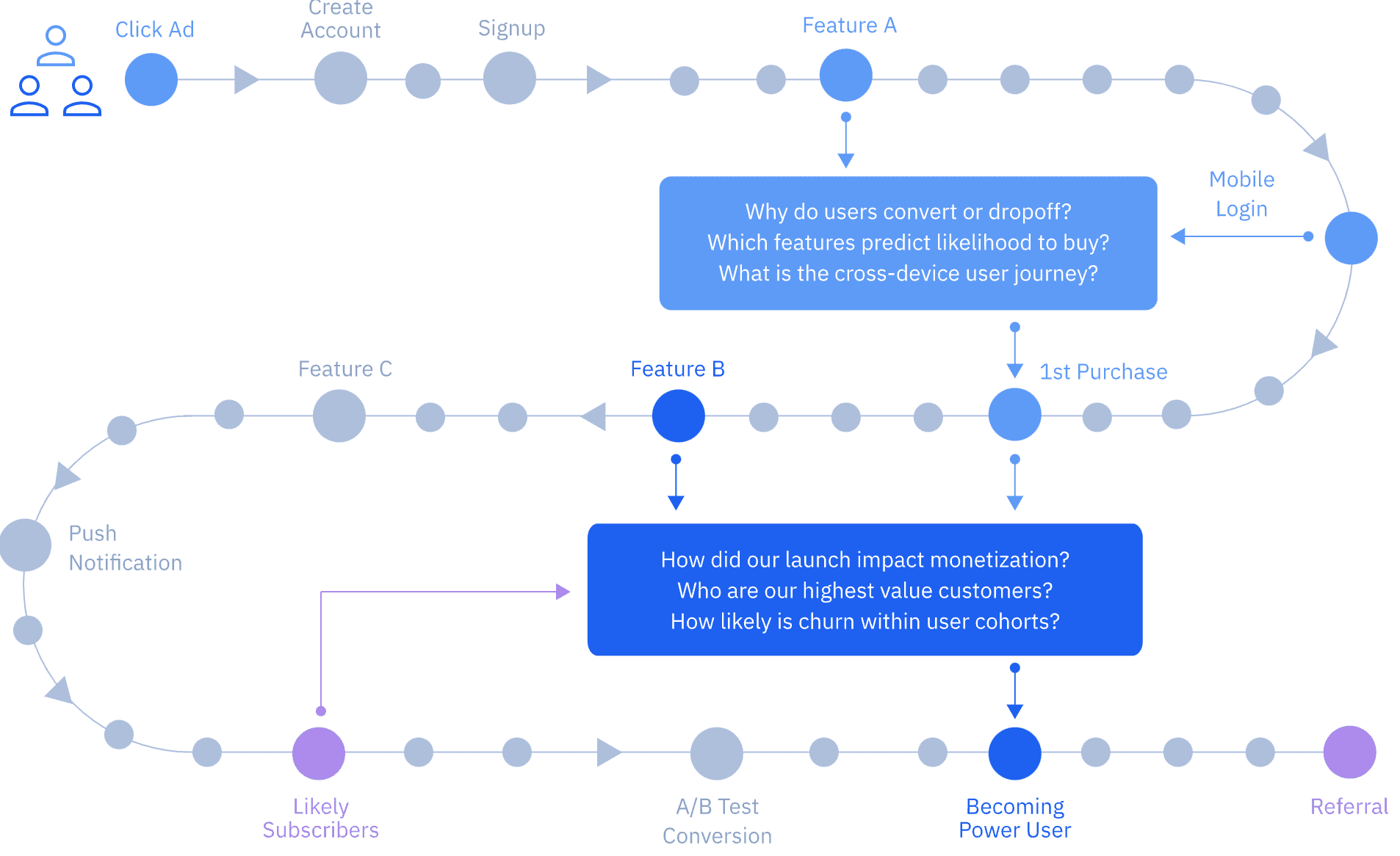
Amplitude will give you data and feedback to guide your product development process. Use Amplitude to give your team information on customer behavior and experience and understand feature adoption, user engagement, and customer retention. Get valuable information that will help you generate ideas grounded in real data, develop products more effectively, and analyze existing products for opportunities for improvement.
Atlassian
Atlassian makes tools to help your agile development team stay organized and on the same page. Their software, Jira, will help you track bugs and optimize your product. It also has tools like Jira Core that enable communication and collaboration with your non-technical teams.
Productboard
To use customer feedback data most effectively, you want to track and keep it organized. Productboard has many features to help you, including boards for prioritization, insights, and user engagement. No matter where you’re getting your customer data from, Productboard gives you a single place to consolidate feedback and gain actionable insights. You can use it to create a product roadmap and share data among your entire team.
Asana
Collaboration is essential for effective product development, and Asana is a project management tool that focuses on organized, successful team collaboration. You can use their templates to build product roadmaps for your team. You can also track bugs, collect customer feedback, and keep everyone focused on team goals and objectives.
Figma
Whether you’re prototyping, doing an intensive design sprint, or getting feedback from your teams, Figma will be a useful tool for the design and development of your product. Collaborative feedback tools like FigJam make it easy for all your teams to collaborate on design, even those unfamiliar with design software. You can live-prototype directly in the program and use those prototypes in research and user testing.
Analytics are crucial for excellent product development
As we’ve seen, leading companies use data to support their product development. Digital analytics tools are how you get data you can trust. To boost your analytics knowledge, regardless of your skill level, check out our round-up of digital analytics resources.
Product development reading list
- The Case For The Innovative Product Manager Forrester
- 15 Metaphors for Waste In Product Development John Cutler
- Optimize the Product Life Cycle With Data-Driven Decisions Gartner
Thinking about your next product development roadmap? Make sure you’ve identified the right metrics with our North Star playbook.

Patrick Thompson
Former Director of Product Management, Amplitude
Patrick Thompson is a former director of product for Amplitude and co-founded Iteratively, acquired by Amplitude. Previously, he was design manager at Atlassian and lead designer at Syncplicity.
More from Patrick