Using formula metrics in Experiment Results
In an Experiment Results chart, using a formula metric offers you greater flexibility when performing analyses. A formula metric is a metric that consists of:
- At least one event, and
- A mathematical operation through which the events interact with each other.
If you've used custom formulas in Event Segmentation, this should be familiar to you. If not, take review that article before proceeding.
Create a formula metric
To add a formula metric to your Experiment Results chart
- In the Primary Metric module, click Add Metric and choose a formula from the Formula dropdown options.
- Click Define single-use metric, then select Formula from the Metric Type dropdown.
- Click Select event... to begin selecting events to include in your formula metric. Repeat this step until you've selected all the events you need.
- In the Formula box, enter the formula for calculating your formula metric. Click here for a list of formulas Experiment Results supports, or here or an explanation of formula syntax.
- Add a name for this new formula metric and then click Apply. The metric now appears in your Experiment Results chart.
You can also view this metric in the object management center.
Supported formula functions
Experiment Results supports the formula functions listed here:
UNIQUES
Syntax: UNIQUES(event)
- Event: Refers to the event you're interested in. This must be a letter corresponding to an event in the Events Module. Returns the number of unique users who triggered the event.
TOTALS
Syntax: TOTALS(event)
- Event: Refers to the event you're interested in. This must be a letter corresponding to an event in the Events Module. Returns the total number of times users triggered the event.
PROPSUM
Syntax: PROPSUM(event)
- Event: Refers to the event you're interested in. This must be a letter corresponding to an event in the Events Module.
This function only works when grouping by a numerical property on the event. If grouping by multiple properties, the formula runs the calculation with the first group-by clause.
Returns the sum of the property values you're grouping the specified event by.
PROPAVG
Syntax: PROPAVG(event)
- Event: Refers to the event you're interested in. This must be a letter corresponding to an event in the Events Module.
This function only works when grouping by a numerical property on the event. If grouping by multiple properties, the formula runs the calculation with the first group-by clause.
Returns the average of the property values you're grouping by. This function is the same as PROPSUM(event)/TOTALS(event). Learn more about how Amplitude calculates PROPAVG and PROPSUM in this article
PROPCOUNTAVG
Syntax: PROPCOUNTAVG(event)
- Event: Refers to the event that interests you. This must be a letter that corresponds to an event in the Events card. If grouping by multiple properties, the formula runs the calculation with the first group-by clause. Returns the average number of distinct values each user has for a specified property.
For example, imagine you're interested in the average number of song genres your music app subscribers listen to. Every time a user plays a song, a Play Song or Video event triggers; each played song also captures a Genre_Type event property. Running PROPCOUNTAVG on Play Song or Video grouped by Genre_Type gives you the average number of unique Genre_Type values users who fire PlaySong or Video have.
Note
PROPCOUNTAVG supports only numeric event properties in Experiment.PROPMAX
Syntax: PROPMAX(event)
- Event: Returns the maximum value of the property you're grouping the specified event by. The property must be numeric. If grouping by multiple properties, the calculation uses the first group-by clause.
PROPMIN
Syntax: PROPMIN(event)
- Event: Returns the minimum value of the property you're grouping the specified event by. The property must be numeric. If grouping by multiple properties, the calculation uses the first group-by clause.
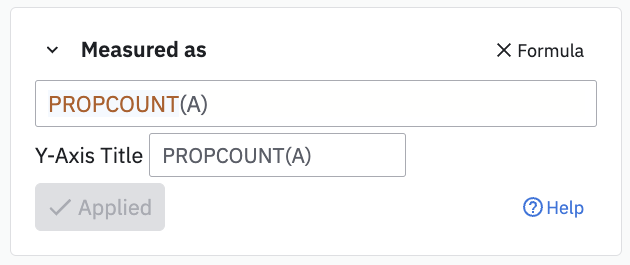
PROPCOUNT
Syntax: PROPCOUNT(event)
- Event: Refers to the event that interests you. This must be a letter that corresponds to an event in the Events card. If grouping by multiple properties, the formula runs the calculation with the first group by clause.
Returns the number of distinct property values for the property by which the event is grouped. In this setup, the formula retrieves the number of different departments covering all the items for which details were viewed:
PROPCOUNT is an estimate of distinct property values. This estimate comes from a HyperLogLog algorithm, and its accuracy depends on amount of data it has to work with. Expect a relative error in the range of 0.1% for less than 12,000 unique values and up to 0.5% for more than 12,000 unique property values, depending on the cardinality of the property.
Note
PROPCOUNT supports only numeric event properties in Experiment.A common metric used in experiments is the number of distinct days someone does an event. To compute this metric, use PROPCOUNT and specify an event property that's a number. For example, the YYYYMMDD format for a date. You may need to use a derived property to make sure you apply the PROPCOUNT to a number.
REVENUETOTAL
Syntax: $:REVENUETOTAL(event)
- Event: Refers to the revenue event. This must be a letter that corresponds to an event in the Event card.
- This function only works if you are grouping by a numerical property on the event.
Returns the aggregate sum of the property, formatted as a currency. It's the same as PROPSUM(event). The $: prefix is optional. Its presence ensures the output format is a currency.
Formula syntax
In your formulas, refer to events selected in the Events Module by their corresponding letter. The functions and the parameters aren't case-sensitive. You can also perform the following arithmetic operations:
- Parenthesis ()
- Addition (+)
- Subtraction (-)
- Multiplication (*)
- Division (/)
Formula metric examples
Use these examples to create common business metrics for your experiments. Each example shows the formula syntax and what it measures.
Total engagement score
Combines multiple engagement events into a single metric.
Formula: TOTALS(A) + TOTALS(B) + TOTALS(C)
Example: If event A is "Article Read", event B is "Comment Posted", and event C is "Article Shared", this formula sums all engagement actions.
Average order value
Calculates the average value of orders or purchases.
Formula: PROPAVG(A)
Example: If event A is "Purchase Completed" grouped by a order_value property, this formula returns the average order value. This is equivalent to PROPSUM(A) / TOTALS(A).
Engagement ratio
Compares two types of engagement to understand user preferences.
Formula: TOTALS(A) / TOTALS(B)
Example: If event A is "Video Watched" and event B is "Article Read", this formula shows the ratio of video views to article reads.
How Amplitude calculates experiment data for formula metrics
Before getting into how calculations of formula metrics work with experiment data, it’s important to understand the Experiment Analysis view, which provides details for your experiment.
For formula metrics, Amplitude computes the results for each function independently to find the mean and variance of each one. It then applies the arithmetic operators to the results of these individual functions.
For example: You've defined a formula metric as TOTALS(A) + TOTALS(B). Amplitude calculates the variances and means of both components of this metric, as well as the covariance.
If you set X equal to TOTALS(A) and Y equal to TOTALS(B), the following statements hold:
-
V[X]= Variance of X -
E[X]= Mean of X -
V[Y]= Variance of Y -
E[Y]= Mean of Y -
Cov[X, Y]= Covariance of X and Y, assumed to be zero for all mathematical operations. -
Addition: Variance:
V[X + Y] = nV[X] + nV[Y]
Mean:E[X + Y] = E[X] + E[Y] -
Subtraction: Variance:
V[X - Y] = nV[X] + nV[Y]
Mean:E[X - Y] = E[X] - E[Y] -
Multiplication: Variance:
V[X * Y] = n^3 mu_y^2 sigma_x^2 + n^3 sigma_y^2 mu_x^2 + n^2 sigma_x^2 sigma_y^2
Mean:E[X * Y] = E[X] * E[Y] -
Division: Variance:
Mean:
E[X / Y] = E[X] / E[Y]
After you have the mean and variance of the formula metric, you can calculate the confidence interval chart and the p-values.
Formula / Metric: TOTALS(A) / TOTALS(B)
November 14th, 2024
Need help? Contact Support
Visit Amplitude.com
Have a look at the Amplitude Blog
Learn more at Amplitude Academy
© 2026 Amplitude, Inc. All rights reserved. Amplitude is a registered trademark of Amplitude, Inc.